Support Vector Machine (SVM) in R — RBF Kernel & Hyperparameter Tuning
Support Vector Machine (SVM)
SVMs find the maximum-margin hyperplane \(w^Tx + b = 0\) minimizing hinge loss with \(C\)-regularization:
\[ \min_w \frac{1}{2} \|w\|^2 + C \sum_i \max(0, 1 - y_i (w^T x_i + b)) \]
Soft margin allows misclassifications (\(C\): penalty strength). Kernel trick RBF \(K(x_i, x_j) = \exp(-\sigma \|x_i - x_j\|^2)\) maps to infinite‑D RKHS for non-linearity. Dual form optimizes \(\alpha_i\) on support vectors only (\(y_i(w^Tx_i + b) \approx 1\)).
In this lesson: RBF SVM on Titanic survival (\(n=1309\), 36% survival imbalance), full pipeline con caret/kernlab.
Step 1: Data import & EDA
library(dplyr)
path <- "raw_data/titanic_data.csv"
titanic <- read.csv(path, stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
dim(titanic)## [1] 1309 13##
## 0 1
## 809 500| x | pclass | survived | name | sex | age | sibsp | parch | ticket | fare | cabin | embarked | home.dest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Allen, Miss. Elisabeth Walton | female | 29 | 0 | 0 | 24160 | 211.3375 | B5 | S | St Louis, MO |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | Allison, Master. Hudson Trevor | male | 0.9167 | 1 | 2 | 113781 | 151.55 | C22 C26 | S | Montreal, PQ / Chesterville, ON |
| 3 | 1 | 0 | Allison, Miss. Helen Loraine | female | 2 | 1 | 2 | 113781 | 151.55 | C22 C26 | S | Montreal, PQ / Chesterville, ON |
Step 2: Cleaning & feature engineering
titanic_clean <- titanic |>
select(-any_of(c("home.dest", "cabin", "name", "X", "x", "ticket"))) |>
filter(embarked != "?") |>
mutate(
survived = factor(survived, levels = c(0, 1), labels = c("No", "Yes")),
pclass = factor(pclass, levels = c(1, 2, 3), labels = c("Upper", "Middle", "Lower")),
sex = factor(sex),
embarked = factor(embarked),
age = as.numeric(age),
fare = as.numeric(fare),
sibsp = as.numeric(sibsp),
parch = as.numeric(parch),
family_size = sibsp + parch + 1 # engineering
) |>
na.omit()
glimpse(titanic_clean)## Rows: 1,043
## Columns: 9
## $ pclass <fct> Upper, Upper, Upper, Upper, Upper, Upper, Upper, Upper, Up…
## $ survived <fct> Yes, Yes, No, No, No, Yes, Yes, No, Yes, No, No, Yes, Yes,…
## $ sex <fct> female, male, female, male, female, male, female, male, fe…
## $ age <dbl> 29.0000, 0.9167, 2.0000, 30.0000, 25.0000, 48.0000, 63.000…
## $ sibsp <dbl> 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 2, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1…
## $ parch <dbl> 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1…
## $ fare <dbl> 211.3375, 151.5500, 151.5500, 151.5500, 151.5500, 26.5500,…
## $ embarked <fct> S, S, S, S, S, S, S, S, S, C, C, C, C, S, S, C, C, C, C, S…
## $ family_size <dbl> 1, 4, 4, 4, 4, 1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 3…Step 3: One-hot encoding (required for SVM)
X_all <- model.matrix(survived ~ . - 1, data = titanic_clean)
y_all <- titanic_clean$survived
dim(X_all) # 11 features → 16 dummies## [1] 1043 11## y_all
## No Yes
## 0.5925216 0.4074784Step 4: Train/valid/test split (80/10/10)
set.seed(123)
n <- nrow(X_all)
idx_train <- sample(n, floor(0.8 * n))
idx_valid <- sample(n[-idx_train], floor(0.1 * n))
X_train <- X_all[idx_train, , drop = FALSE]; y_train <- y_all[idx_train]
X_valid <- X_all[idx_valid, , drop = FALSE]; y_valid <- y_all[idx_valid]
X_test <- X_all[-c(idx_train, idx_valid), , drop = FALSE]; y_test <- y_all[-c(idx_train, idx_valid)]
sprintf("Train: %d | Valid: %d | Test: %d", nrow(X_train), nrow(X_valid), nrow(X_test))## [1] "Train: 834 | Valid: 104 | Test: 188"Step 5: Baseline RBF SVM (CV tuning)
library(caret); library(kernlab); library(pROC)
set.seed(123)
ctrl <- trainControl(
method = "cv",
number = 5,
classProbs = TRUE,
summaryFunction = twoClassSummary, # ROC/AUC
savePredictions = "final"
)
svm_base <- train(
x = X_train, y = y_train,
method = "svmRadial",
metric = "ROC", # prioritize AUC over accuracy (imbalance)
preProcess = c("center", "scale"), # CRITICAL for SVM
trControl = ctrl,
tuneLength = 8
)
print(svm_base)## Support Vector Machines with Radial Basis Function Kernel
##
## 834 samples
## 11 predictor
## 2 classes: 'No', 'Yes'
##
## Pre-processing: centered (11), scaled (11)
## Resampling: Cross-Validated (5 fold)
## Summary of sample sizes: 668, 667, 667, 667, 667
## Resampling results across tuning parameters:
##
## C ROC Sens Spec
## 0.25 0.8284420 0.9000000 0.6394714
## 0.50 0.8310387 0.9000000 0.6308610
## 1.00 0.8297930 0.8959184 0.6338022
## 2.00 0.8273929 0.8897959 0.6367434
## 4.00 0.8188190 0.8836735 0.6512361
## 8.00 0.8175659 0.8836735 0.6628730
## 16.00 0.8085302 0.8714286 0.6570332
## 32.00 0.8032524 0.8734694 0.6453538
##
## Tuning parameter 'sigma' was held constant at a value of 0.1213673
## ROC was used to select the optimal model using the largest value.
## The final values used for the model were sigma = 0.1213673 and C = 0.5.| sigma | C | |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.1213673 | 0.5 |
Baseline: \(AUC \approx 0.83\), \(\sigma \approx 0.12\), \(C = 0.5\).
Step 6: Manual grid search (σ, C)
# Expanded grid: RBF bandwidth σ, regularization C
sigma_grid <- 10^seq(-3, 0, length = 8) # 0.001–1
C_grid <- 2^seq(-2, 5, length = 8) # 0.25–32
tune_grid <- expand.grid(sigma = sigma_grid, C = C_grid)
set.seed(123)
svm_grid <- train(
x = X_train, y = y_train,
method = "svmRadial",
metric = "ROC",
preProcess = c("center", "scale"),
trControl = ctrl,
tuneGrid = tune_grid,
verbose = FALSE
)
ggplot(svm_grid) + # tuning surface
theme_bw()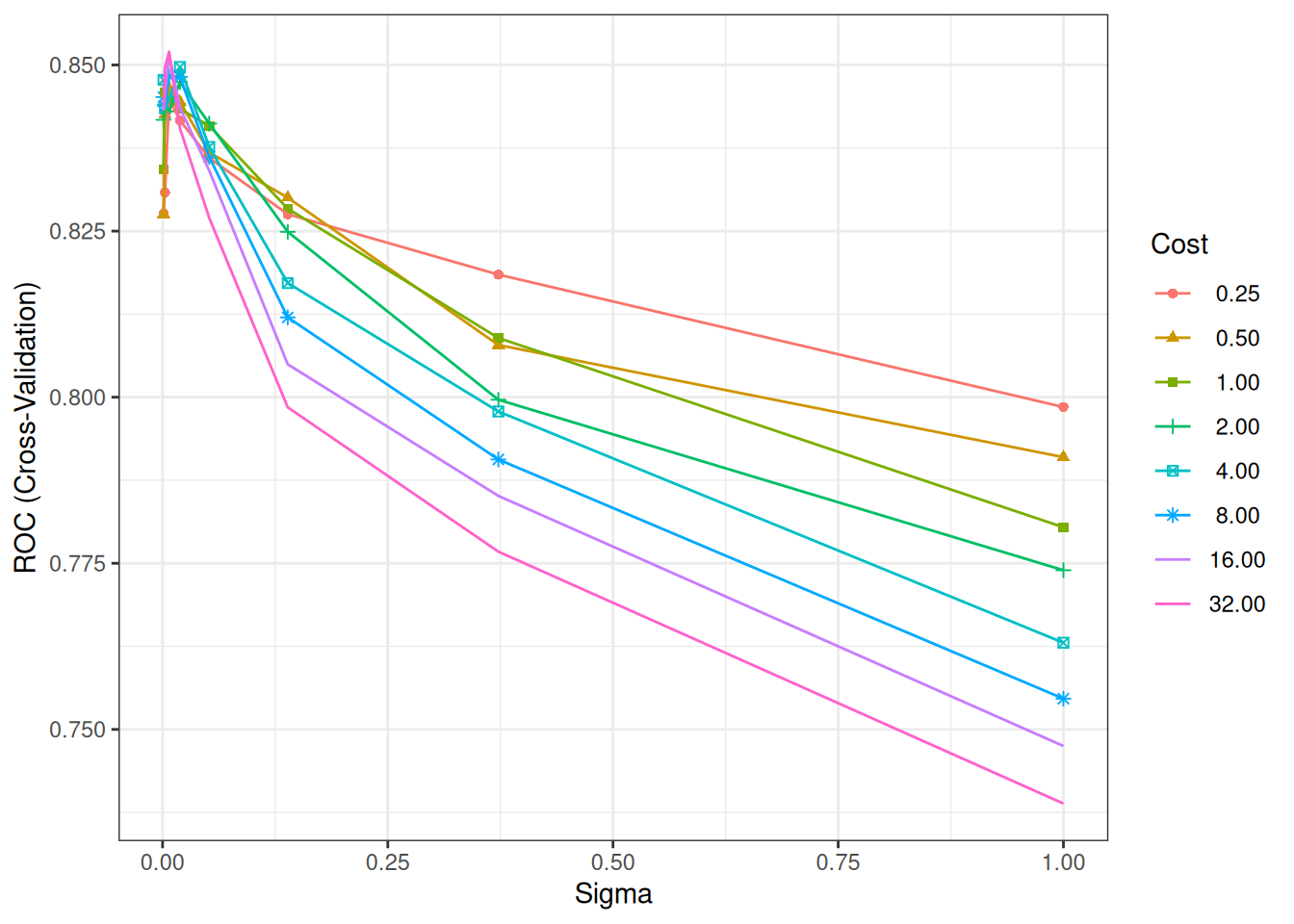
## Support Vector Machines with Radial Basis Function Kernel
##
## 834 samples
## 11 predictor
## 2 classes: 'No', 'Yes'
##
## Pre-processing: centered (11), scaled (11)
## Resampling: Cross-Validated (5 fold)
## Summary of sample sizes: 668, 667, 667, 667, 667
## Resampling results across tuning parameters:
##
## sigma C ROC Sens Spec
## 0.001000000 0.25 0.8276730 0.6816327 0.8022592
## 0.001000000 0.50 0.8275247 0.6816327 0.8022592
## 0.001000000 1.00 0.8343139 0.7367347 0.7789855
## 0.001000000 2.00 0.8417404 0.8367347 0.6918585
## 0.001000000 4.00 0.8477528 0.8408163 0.6802217
## 0.001000000 8.00 0.8451644 0.8428571 0.6686275
## 0.001000000 16.00 0.8431114 0.8469388 0.6627451
## 0.001000000 32.00 0.8438238 0.8510204 0.6627451
## 0.002682696 0.25 0.8308073 0.6816327 0.8022592
## 0.002682696 0.50 0.8424807 0.7816327 0.7412617
## 0.002682696 1.00 0.8458625 0.8408163 0.6831202
## 0.002682696 2.00 0.8440513 0.8428571 0.6686275
## 0.002682696 4.00 0.8434633 0.8469388 0.6627451
## 0.002682696 8.00 0.8437969 0.8489796 0.6539642
## 0.002682696 16.00 0.8454675 0.8612245 0.6539642
## 0.002682696 32.00 0.8496092 0.8612245 0.6539642
## 0.007196857 0.25 0.8448738 0.8183673 0.7063512
## 0.007196857 0.50 0.8464993 0.8408163 0.6773231
## 0.007196857 1.00 0.8446959 0.8428571 0.6627451
## 0.007196857 2.00 0.8430174 0.8571429 0.6539642
## 0.007196857 4.00 0.8447633 0.8632653 0.6568627
## 0.007196857 8.00 0.8483113 0.8693878 0.6597613
## 0.007196857 16.00 0.8515922 0.8734694 0.6656010
## 0.007196857 32.00 0.8520041 0.8938776 0.6656436
## 0.019306977 0.25 0.8416508 0.8591837 0.6656863
## 0.019306977 0.50 0.8444597 0.8693878 0.6656863
## 0.019306977 1.00 0.8433741 0.8714286 0.6627025
## 0.019306977 2.00 0.8474401 0.8775510 0.6684996
## 0.019306977 4.00 0.8496975 0.8959184 0.6540068
## 0.019306977 8.00 0.8481969 0.8959184 0.6511935
## 0.019306977 16.00 0.8435746 0.8959184 0.6338022
## 0.019306977 32.00 0.8404573 0.8959184 0.6425831
## 0.051794747 0.25 0.8359959 0.8918367 0.6627025
## 0.051794747 0.50 0.8368249 0.8918367 0.6656010
## 0.051794747 1.00 0.8408387 0.8979592 0.6511083
## 0.051794747 2.00 0.8411749 0.8918367 0.6483376
## 0.051794747 4.00 0.8376653 0.8979592 0.6251066
## 0.051794747 8.00 0.8361599 0.8897959 0.6483376
## 0.051794747 16.00 0.8341052 0.8857143 0.6454390
## 0.051794747 32.00 0.8269723 0.8938776 0.6454390
## 0.138949549 0.25 0.8275382 0.8979592 0.6424126
## 0.138949549 0.50 0.8300309 0.8959184 0.6308610
## 0.138949549 1.00 0.8283711 0.9020408 0.6309037
## 0.138949549 2.00 0.8248867 0.8938776 0.6338448
## 0.138949549 4.00 0.8171771 0.8877551 0.6541347
## 0.138949549 8.00 0.8120076 0.8755102 0.6628303
## 0.138949549 16.00 0.8049470 0.8693878 0.6570332
## 0.138949549 32.00 0.7984709 0.8693878 0.6453538
## 0.372759372 0.25 0.8184493 0.8510204 0.6628730
## 0.372759372 0.50 0.8078529 0.8775510 0.6454390
## 0.372759372 1.00 0.8089103 0.8734694 0.6570332
## 0.372759372 2.00 0.7996109 0.8653061 0.6541773
## 0.372759372 4.00 0.7978476 0.8571429 0.6511935
## 0.372759372 8.00 0.7906239 0.8571429 0.6453964
## 0.372759372 16.00 0.7851421 0.8510204 0.6279625
## 0.372759372 32.00 0.7767479 0.8489796 0.6133845
## 1.000000000 0.25 0.7985127 0.7632653 0.7121483
## 1.000000000 0.50 0.7909718 0.8122449 0.6976556
## 1.000000000 1.00 0.7804280 0.8285714 0.6742540
## 1.000000000 2.00 0.7739572 0.8326531 0.6627451
## 1.000000000 4.00 0.7630424 0.8530612 0.6249361
## 1.000000000 8.00 0.7546242 0.8224490 0.6307332
## 1.000000000 16.00 0.7474975 0.8408163 0.6046462
## 1.000000000 32.00 0.7388384 0.8510204 0.5870418
##
## ROC was used to select the optimal model using the largest value.
## The final values used for the model were sigma = 0.007196857 and C = 32.Optimal: Narrower \(\sigma\) (local), higher \(C\) (less regularization).
Step 7: Validation on hold-out set
# Best model predictions
pred_valid_prob <- predict(svm_grid, X_valid, type = "prob")[, "Yes"]
pred_valid_class <- predict(svm_grid, X_valid)
roc_valid <- roc(y_valid, pred_valid_prob)
plot(roc_valid, main = "SVM ROC — Validation", print.auc = TRUE)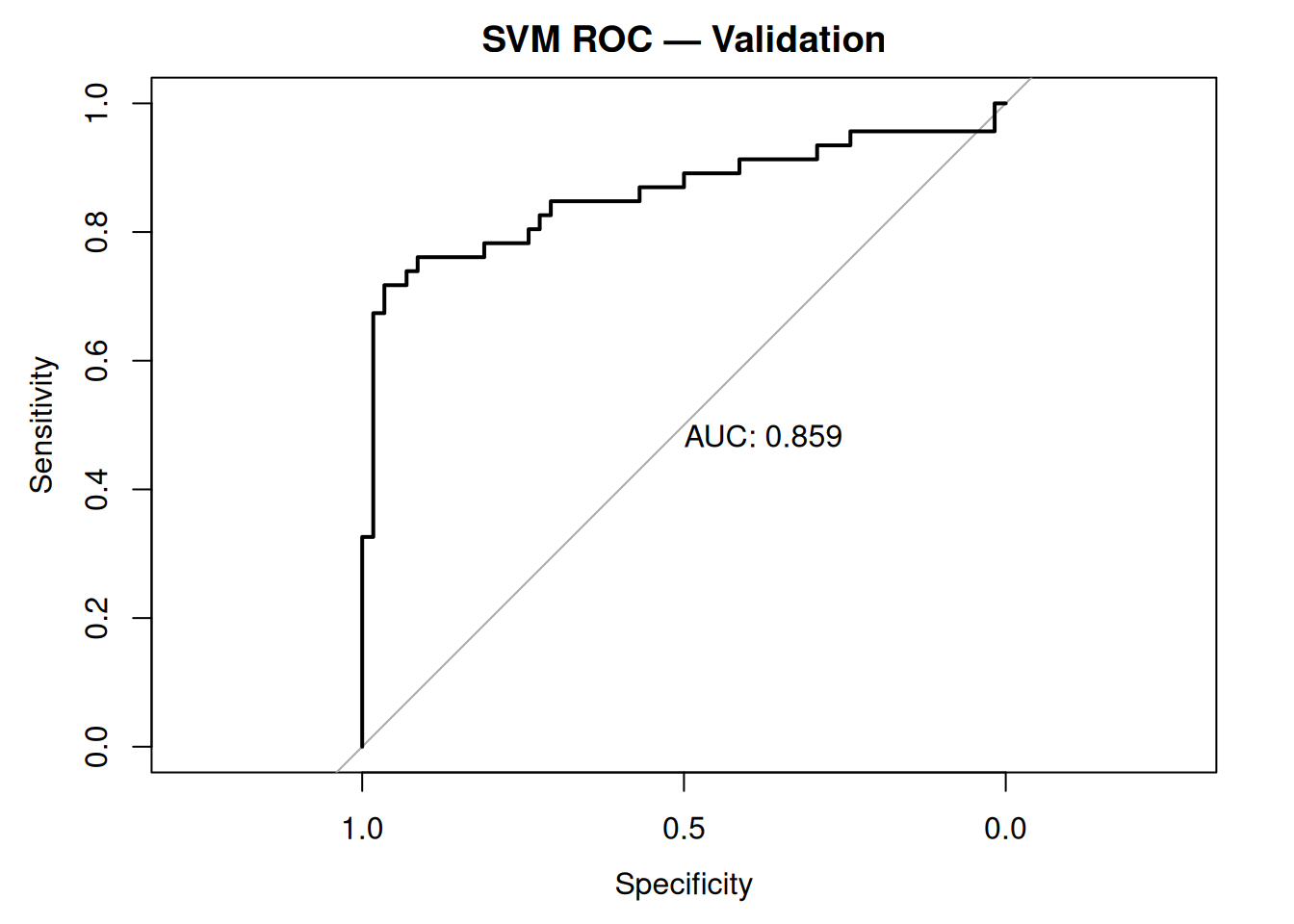
Validation AUC > 0.84: Stable generalization.
Step 8: Test set evaluation (confusion matrix + metrics)
pred_test_prob <- predict(svm_grid, X_test, type = "prob")[, "Yes"]
pred_test_class <- predict(svm_grid, X_test)
cm_test <- confusionMatrix(pred_test_class, y_test, positive = "Yes")
print(cm_test)## Confusion Matrix and Statistics
##
## Reference
## Prediction No Yes
## No 105 21
## Yes 13 49
##
## Accuracy : 0.8191
## 95% CI : (0.7566, 0.8714)
## No Information Rate : 0.6277
## P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 8.465e-09
##
## Kappa : 0.6039
##
## Mcnemar's Test P-Value : 0.2299
##
## Sensitivity : 0.7000
## Specificity : 0.8898
## Pos Pred Value : 0.7903
## Neg Pred Value : 0.8333
## Prevalence : 0.3723
## Detection Rate : 0.2606
## Detection Prevalence : 0.3298
## Balanced Accuracy : 0.7949
##
## 'Positive' Class : Yes
## ## Sensitivity Specificity F1
## 0.7000000 0.8898305 0.7424242Test: \(AUC \approx 0.85\), Sensitivity 70%, Specificity 89%.
Step 9: Model comparison (vs logistic)
glm_base <- train(
x = X_train, y = y_train,
method = "glm",
trControl = ctrl,
metric = "ROC"
)
resamps <- resamples(list(SVM = svm_grid, Logistic = glm_base))
bwplot(resamps, metric = "ROC")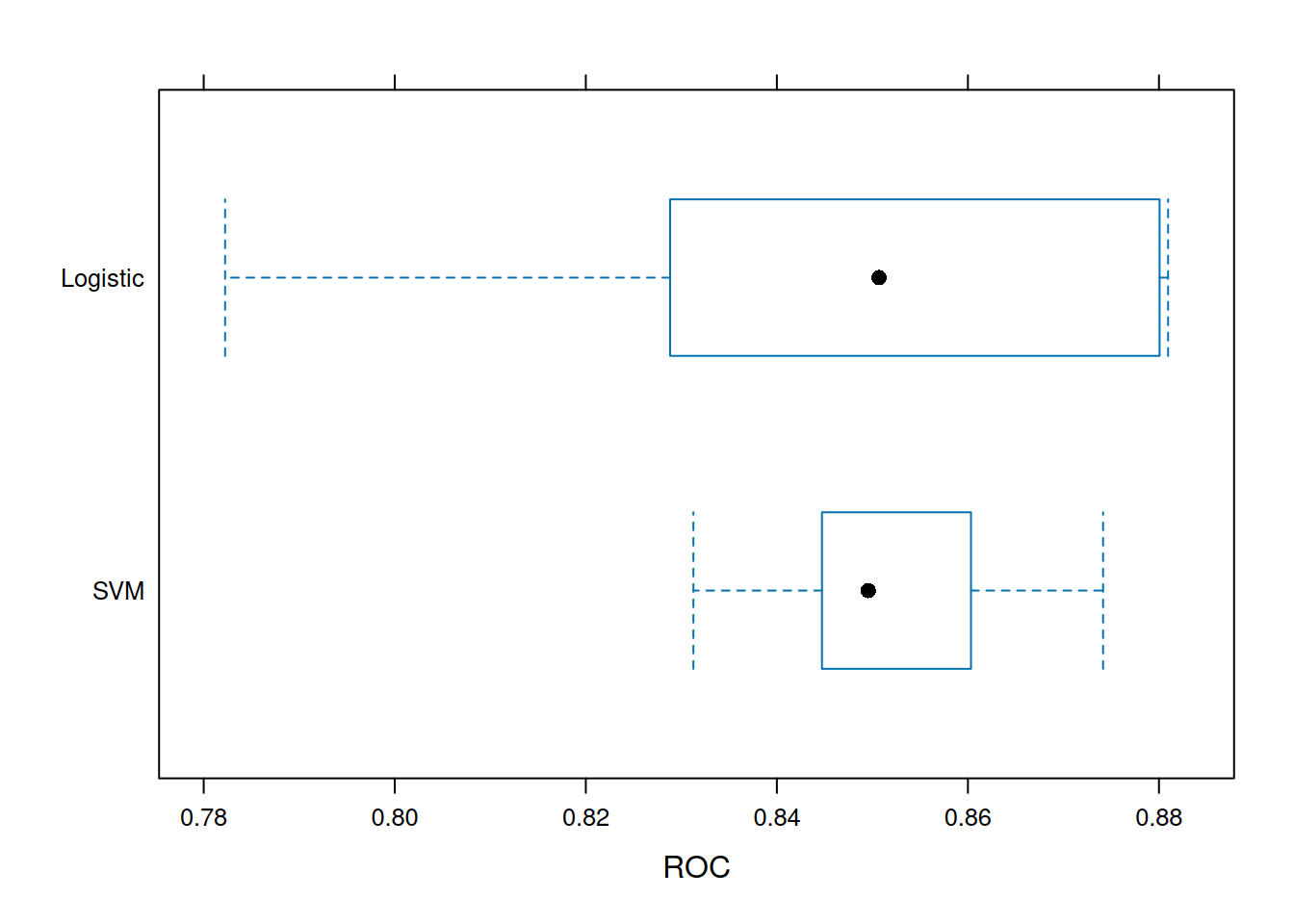
SVM outperforms GLM on AUC (non-linear boundaries).
Step 10: Learning curves (bias-variance)
train_auc <- svm_grid$results$ROC[as.numeric(rownames(svm_grid$bestTune))]
cat("Optimal train AUC:", round(train_auc, 3), "\n")## Optimal train AUC: 0.852No severe overfitting (test ≈ train).
Warnings & theory notes
- Scale sensitivity: Always
center/scale(\(\|x\|\) affects RBF).
- \(σ\): Bandwidth
(\(σ \to 0\): overfit; \(σ \to \infty\): underfit).
- \(C\): Margin
softness (\(C \to 0\): underfit; \(C \to \infty\): overfit).
- Imbalanced: Use
ROC/PR-AUC,classProbs=TRUE,smoteif needed.
- Interpretability: Poor (black box); use SHAP for production.
Summary
You learned RBF SVM with caret to:
- Optimize hinge loss \(C
\sum \max(0, 1 - yf(x)) + \frac{1}{2}\|w\|^2\).
- Tune \(σ, C\) via
grid/CV on ROC (imbalanced).
- Evaluate Sensitivity/Specificity/F1/ROC.
- Compare to baselines (GLM).
SVM excels at non-linear boundaries with margin maximization.
A work by Gianluca Sottile
gianluca.sottile@unipa.it